Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) with OTP: Analyzing the Difference Between SMS OTP and App OTP (Authenticator) – Which is Optimal?
Security is paramount in the digital world. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) has become the gold standard for protecting accounts against cyberattacks and fraud. Among various 2FA methods, OTP (One-Time Password) is the most common, utilizing two primary delivery methods: SMS OTP (via text message) and App OTP (via authentication apps like Google Authenticator).
This article, compiled by security experts at OTPNhanh, delves deep into the mechanisms, advantages, disadvantages, and potential risks of both methods. The goal is to help you understand the core concepts and make the optimal two-factor authentication choice for each account type and usage need.
1. Core Definitions: Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) and OTP
1.1. What is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
Two-Factor Authentication is a security process that requires the user to provide two independent verification factors to access an account. These factors are typically divided into 3 categories:
-
Knowledge Factor: Something only you know (Password, PIN).
-
Possession Factor: Something only you have (Phone, Security Key, Bank card).
-
Inherence Factor: Something inherent to you (Fingerprint, Face recognition).
The OTP code represents the Possession Factor, used in conjunction with your Password (Knowledge Factor) to complete the 2FA process.
1.2. OTP (One-Time Password) and Time Sensitivity
The OTP is a random string of characters, valid for only one single use within a short timeframe. Unlike static passwords, the OTP code constantly changes, eliminating the risk of being stolen and reused (Replay Attack).

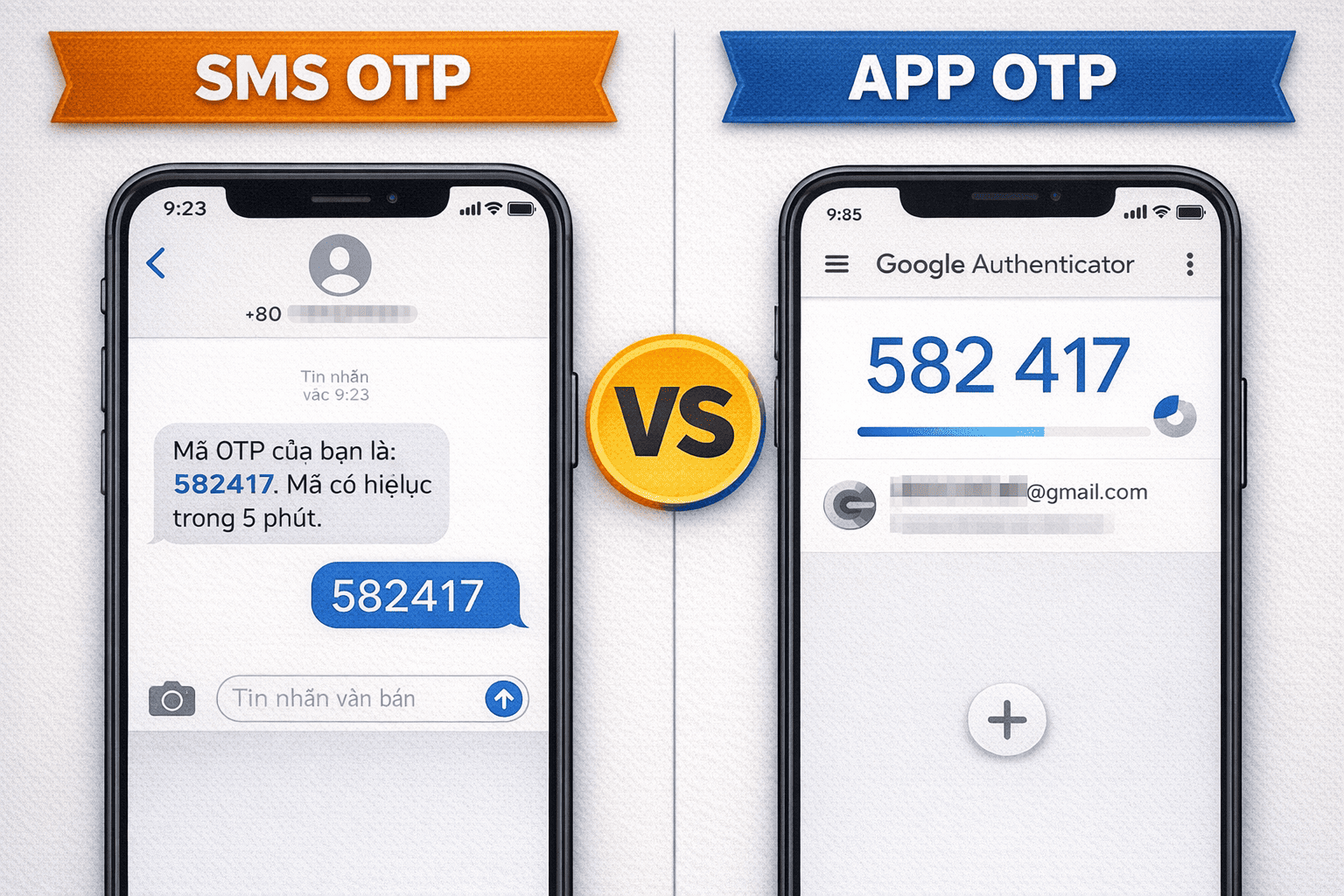
2. Method 1: SMS OTP – Popularity and Sim Swap Risk
SMS OTP is the oldest and most widespread two-factor authentication method, where the OTP code is transmitted via a text message to your registered phone number.
2.1. How SMS OTP Works
-
Request: The user enters their static password and requests the OTP code to be sent.
-
Generate & Send: The server generates the code and sends it via an SMS Gateway to the mobile carrier.
-
Receive: The code is delivered to the user's phone via the cellular network.
-
Verify: The user enters the code to complete the verification.
2.2. Advantages of SMS OTP
-
High Accessibility: Almost everyone owns a mobile phone and uses SMS service; no app installation or Internet connection is required.
-
Ease of Use: Simple procedure, requires no complex setup.
2.3. Disadvantages and Critical Security Risks
-
Sim Swap Risk: This is the biggest threat. An attacker socially engineers the carrier to switch your phone number to their SIM, thereby intercepting all your incoming SMS OTPs.
-
Code Blocking/Delay: Dependent on the mobile carrier service quality and cellular signal, the OTP code may arrive late or not at all, leading to the "failed to receive OTP" error.
-
International Issues: Difficult to receive OTP codes when traveling abroad or switching SIM cards.

3. Method 2: App OTP (Authenticator) – Optimal Security, Less Flexibility
App OTP is the two-factor authentication method that generates codes through dedicated applications like Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Authy.
3.1. How App OTP (TOTP) Works
App OTP uses the TOTP (Time-based One-Time Password) algorithm:
-
Setup: Upon 2FA activation, the app and the server share an initial Secret Key (often displayed as a QR code).
-
Code Generation: The app independently generates the OTP code based on the Secret Key and the Current Time.
-
Usage: The user enters the code shown on the app. The server also independently calculates the code based on the same Secret Key and time.
Note: This code generation process does not require an Internet connection or cellular signal; the code is generated locally on your device.
3.2. Advantages of App OTP
-
Higher Security: Immune to Sim Swap risks and codes being blocked by carriers.
-
International Convenience: Works offline, ideal when traveling internationally.
-
Speed: Codes are generated instantly, avoiding code expiration errors.
3.3. Disadvantages to Consider
-
App Requirement: Requires initial app installation and setup.
-
Risk of Device Loss: If the phone is lost and the Secret Key (Seed) is not backed up, you may permanently lose access to the protected accounts.
-
Lack of Ubiquity: Some services do not support App OTP (e.g., some banks only use SMS OTP).
4. In-Depth Comparison Table: SMS OTP vs. App OTP
| Feature | SMS OTP | App OTP (Authenticator) |
| Possession Factor | Phone number & SIM | Application/Device |
| Relies on Internet/Signal | YES (Needs signal for SMS) | NO (Works Offline) |
| Sim Swap Risk | HIGH (Biggest security risk) | NONE |
| Code Speed | Can be delayed | Instantaneous (On device) |
| Accessibility | Very high | Lower, requires app install |
| Overall Security | Medium | Very high |
| Alternative Solution | OTP Rental (OTPNhanh) | Security Key (FIDO2) |
5. Optimal Solution: Choosing and Combining 2FA with OTP Rental Services
To achieve maximum security, users and businesses must learn how to combine methods flexibly.
5.1. When Should You Use SMS OTP?
-
Less Critical Accounts: Less sensitive services (like forum accounts, newsletters).
-
Business Needs: When needing to rent SIMs for bulk account creation for Marketing purposes, SMS OTP is the only and most economical option.
5.2. When Should You Use App OTP?
-
Most Critical Accounts: Banking, Crypto Exchanges, Primary Email, Cloud Storage.
-
International Users: No worries about roaming fees or cellular signal.
5.3. Utilizing OTPNhanh's OTP Rental Service as a Flexible Security Layer
Our OTP Rental service (using an SMS OTP mechanism via a virtual/temporary phone number) is the perfect solution for:
-
Temporary Needs: For registering trial services, keeping your personal number completely private.
-
Error Recovery: When your main phone number fails to receive OTP, OTP rental provides an instant temporary number to complete the verification.
-
Low Cost & Automated: Low-cost SIM OTP and superior speed compared to traditional SMS OTP.
6. Expert Advice from OTPNhanh
To ensure absolute safety, always adhere to the following principles:
-
Prioritize App OTP: Always prioritize App OTP for financial accounts.
-
Use SMS OTP Smartly: For less critical accounts, use an OTP rental service to protect your personal phone number.
-
Create Strong Passwords: 2FA is only effective when paired with a strong static password.
-
Protect Your SIM Card: Limit providing personal information over the phone to prevent Sim Swap risks.
7. Conclusion: Choosing the Right Security for Your Needs
The OTP code is the lifeline for network security; both SMS OTP and App OTP have their distinct roles. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each type of two-factor authentication helps you make the most informed security decision.
For flexible needs, OTPNhanh's OTP rental service provides the fastest, most secure, and most cost-effective verification solution for all platforms.
📚 Related Articles
To understand more about optimizing verification solutions and costs, you can refer to our specialized articles:
-
Low-Cost OTP Rental: Secrets to Bulk SIM Code Rental & The Most Optimal Price List 2025
-
Comprehensive Solution for SIM Rental Service to Receive Code (OTP/SMS)
-
Rent a Number to Receive OTP: Comprehensive Alternative to Traditional SIMs
-
Fast, Reputable, Low-Cost OTP Rental – Instant Verification Solution 24/7
